Toshiba’s CD5 and CM5 NVMe data centre SSDs are certified for use with DriveScale composable infrastructure.
This infrastructure composes servers on demand from pools of available driveless servers and storage resources.
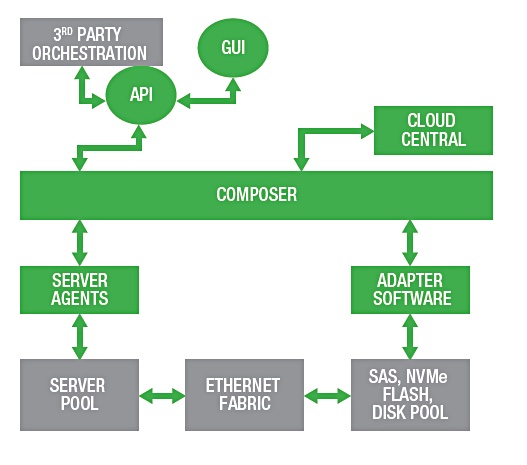
The DriveScale Software Composable Infrastructure uses a software control plane to compose the hardware resources, and return them to the pool when no longer needed. Flash storage resources can be configured by this software at chassis, drive and sub-drive level.
Toshiba said the DriveScale system, using an NVMe-oF link, makes its CD5 and CM5 SSDs fungible, meaning they can be re-used in composed systems. Storage nodes connected to the NVMe-oF protocol enable multiple paths from servers to the CD5 or CM5 SSDs.
Tatsuya Tanaka, VP for ecosystem and standards at Toshiba Memory America, said: “When deployed within the DriveScale Composable Platform, storage services can be delivered with greater performance, resource utilisation, economics and efficiency, all while enabling dynamic service level agreements across workloads.”
DriveScale supports several SSD vendors:
- Intel – D4600 family
- Micron – 9200 products
- Samsung – PM983 and PM1725B families
- Toshiba – KCM51 and now CD5 and CM5 products
- Western Digital – Ultrastar DC SN200 products
The other NAND and SSD supplier, SK hynix, is still qualifying its NVMe SSDs with potential customers, with general availability expected by year-end.
Other composable system developers are Attala Systems, Dell EMC with the MX7000, HPE with Synergy, Liqid and Western Digital.