Cisco and NetApp are adding MAX Data to their FlexPod reference design to make applications run faster.
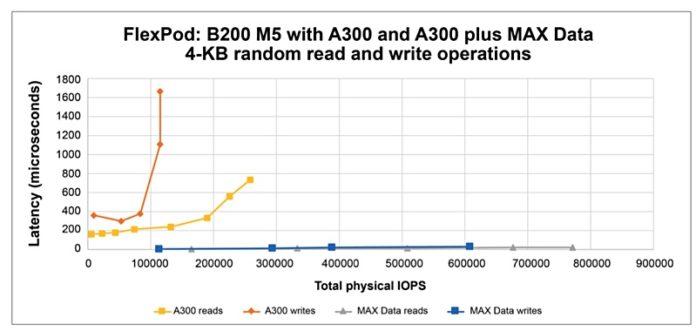
In a white paper published last week Cisco showed MAX Data on FlexPod is capable of delivering five times more I/O operations with 25 times less latency than the same system without MAX Data installed.
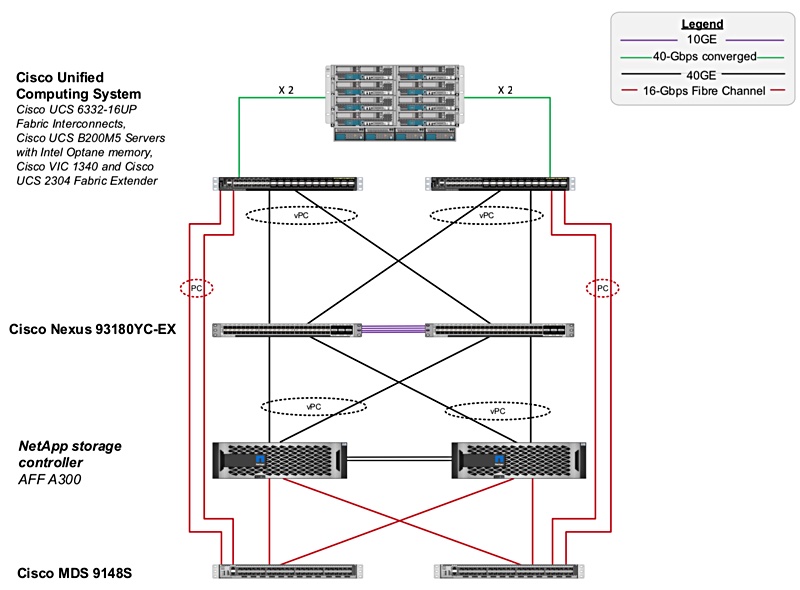
FlexPod is a converged infrastructure (CI) reference platform for compute, storage and networking. It incorporates Cisco validated designs for Cisco UCS servers and Nexus and MDS switches with NetApp’s validated architecture for all-flash and hybrid flash/disk storage arrays running ONTAP software.
MAX Data is NetApp’s Memory Accelerated Data software which uses Optane DIMM caching in servers backed by an all-flash NetApp array. MAX Data presents a POSIX file system interface to applications, which don’t need to change. The software tiers data from the ONTAP all-flash array (treated as an underlying block device) into the Optane persistent memory.
The hottest, most frequently accessed data is kept in the Optane memory space, and cooler, less frequently used, data is tiered to the ONTAP storage array. Most data requests are serviced from Optane with misses serviced from the array.
The array is connected to the Optane DIMMs by an NVMe-oF link. Applications in the server get their data IO requests serviced from the Optane cache/tier instead of the remote NetApp array.
This greatly reduces data access latency times, down to about 10 microseconds from a millisecond or so. Databases can support more transactions with fewer computing resources and complete user queries more quickly.
Design of the times
The FlexPod MAX Data design uses third-generation Cisco UCS 6332-16UP Fabric Interconnects and the UCS virtual interface card with 40Gbit/s Ethernet links to a NetApp AFF A300 storage cluster using vPCs (Virtual Port Channels.)
It supports 16-Gbit/s Fibre Channel, for Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) between the storage cluster and UCS servers.
Optane DIMMS with 128GB, 256GB and 512GB can be used.
The Optane DIMMs must be paired with DRAM DIMMs in each memory channel and can be used in various access modes:
- Memory mode, which provides additional volatile memory capacity.
- App Direct mode, which provides persistence and can be accessed through traditional memory load and store operations.
- Mixed mode where a percentage of the DIMM is used in memory mode and the rest in App Direct mode.
MAX Data uses App Direct mode. For application vendors themselves to use this Optane mode they must rewrite their applications. With MAX Data, applications can use Optane DIMMs without any re-writing of code.