Tom Black, HPE’s new storage boss, is unifying the SimpliVity and Nimble dHCI engineering R&D and laying off an undisclosed number of engineering staff.
HPE said in a statement that the reorganisation will “allow customers to benefit from a consistent and better experience across hybrid cloud, AIOps, support, automation, and lifecycle management for all of their HCI use cases. As part of this plan, there will be a reduction in the HPE HCI headcount, but we’re not disclosing the number of the impacted team members”.
SimpliVity and Nimble dHCI are based on ProLiant servers and managed through InfoSight software. Both are also-rans in the HCI market. It looks as if HPE is saving money by making SimpliVity a variant of Nimble dHCI.
HPE has decided to focus the SimpliVity HCI (hyperconverged infrastructure) on two markets; small and medium business customers and the developing internet edge where the single box approach fits well. The company is calling this ‘edge-optimised HCI’.

This is the first big product move by Tom Black, who was appointed SVP and GM of HPE’s Storage business unit in January. He is a storage outsider, coming from HPE’s acquired Aruba networking business. His 20-year career in networking encompasses a stint as VP Engineering for HP’s networking business, and engineering VP roles at Arista and Cisco.
We’re told he has experience in developing high-performance and scale-out systems with a good customer end-to-end experience.
History
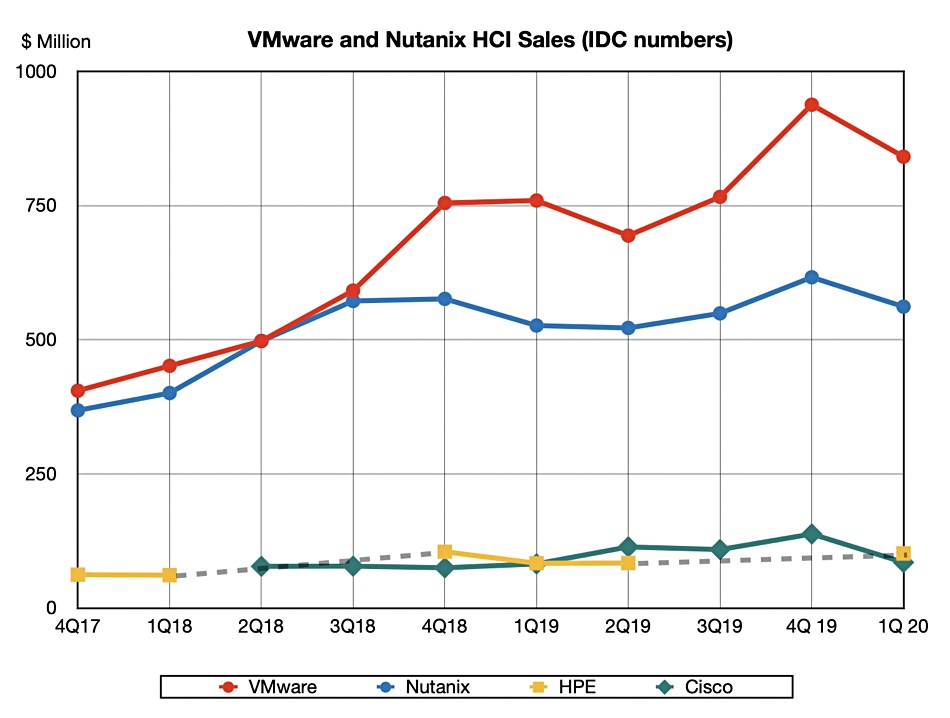
SimpliVity, and HPE overall, is an HCI also-ran, when compared with Dell EMC-VMware and Nutanix.
SimpliVity, based in Westboro, Mass, was founded in 2009, and developed an all-in-one data centre lego box for building IT infrastructure. This combined compute, a hypervisor, storage and basic networking in its single hyperconverged enclosure, and represented a simpler way of scaling IT infrastructure than buying separate servers, storage arrays and networking switches.

Notably, SimpliVity used a hardware acceleration ASIC for data reduction, rendering it a proprietary – as opposed to commodity hardware – system.
Competitors included Nutanix and Springpath, which was bought by Cisco. EMC-owned VMware developed its vSAN product in 2013. Dell bought EMC in 2015 and the HCI industry-dominating EMC VxRail product, based on vSAN, launched in 2016.
HPE bought the SimpliVity business in January 2017 for $650m. It also bought Nimble in March 2017 for $1bn as a smaller SAN array than its 3PAR business but one with the category-defining InfoSight predictive analytics management system.
HPE launched the Nimble disaggregated or dHCI system, with compute nodes sharing an external Nimble storage array, a year ago. At the time, the company said the system scaled compute and storage separately and so was better suited to enterprise workloads than SimpliVity. It was also commodity hardware-based. The system will run mixed workloads including business-critical applications at larger scale than edge-optimised HCI.

SimpliVity development continued with a value-for money focus for smaller businesses. For example, HPE launched a 1U server-based 325 product enclosure using AMD’s EPYC processor, at the same time as the Nimble dHCI product hit the streets.
SimpliVity continued its low-end focus with a revamped 1U SimpliVity 325 using a gen 2 AMD EPYC 7002 series processor and added InfoSight monitoring in October 2019.







