VAST Data is partnering with Vapor IO, a colocation provider of hyperlocal AI platform services in the US, to provide global and multi-format AI data storage, supporting structured and unstructured tabular data, including vectors.
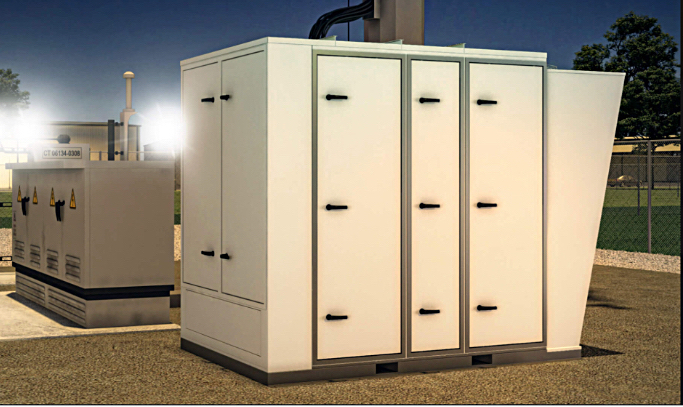
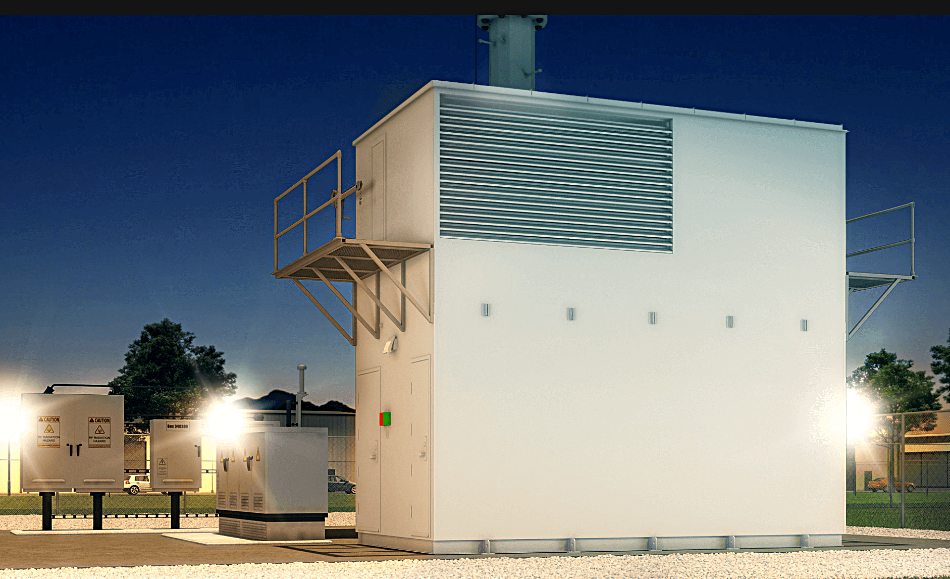
Austin, TX-based Vapor IO has developed self-contained, high-density VEM micro modular datacenters as part of its edge colocation and interconnection facilities, which include both wireless and wired networking capabilities. Its Kinetic Edge combines multi-tenant colocation with software-defined interconnection and high-speed networking.
Vapor IO came out of stealth in 2015, the same year it closed a Series A funding round led by Goldman Sachs. With subsequent B and C-rounds, it has raised $90 million in total.
Zero Gap AI is a Vapor IO-operated 5G and AI-as-a-Service platform, providing private 5G and GPU-based micro-clouds adjacent to specific locations, such as retail stores, factory floors, and city intersections. These are so-called hyperlocal AI services, delivered over private wired and wireless networks without running servers on-premises yet with fast response times.
The local AI site is built from Supermicro servers presenting an Nvidia MGX device, based on the GH200 Grace Hopper superchip, and supporting 5G and AI running on the same machine. There are such sites in 36 US cities, including Atlanta, Chicago, Dallas, Las Vegas, and Seattle, in what Vapor IO calls its Kinetic Grid platform. There are private dedicated wired fiber links to Zero Gap AI customers. An existing last-mile network link could be used as well. A private 5G wireless network can be used inside a customer’s site to link to devices there.

Cole Crawford, Vapor IO’s founder and CEO, stated: “Until now, the challenge has been the high costs and complexities of creating AI clusters in precise locations, not to mention managing the intricate dance of AI orchestration. For those aiming to achieve real-time inferencing, Zero Gap AI presents the ideal architecture. By eliminating the need for onsite AI and 5G hardware and leveraging private fiber from nearby access points, we’re simplifying the process and cutting costs, enabling a seamless adoption and expansion of AI capabilities for businesses and municipalities alike.”
Vapor IO suggests:
- A multi-location retailer can use Zero Gap AI to deploy an AI-driven automated checkout system without putting expensive AI equipment in each store.
- A municipality can use Zero Gap AI computer vision services to deploy a pedestrian safety capability to hundreds of busy intersections without putting equipment on every corner.
- A manufacturer can use Zero Gap AI real-time inferencing to support highly reliable factory IoT, reducing risk and lowering capital expenditures.
The pitch here is that Zero Gap AI provides AI access points “across an entire market” with a distributed architure having mesh-like network grid for AI providing near-zero latency. It is designed for zero downtime and zero congestion. It makes it possible to spin up “AI micro-clouds where they are precisely needed” near to a factory or hospital and both on demand and instantaneously. The data being analyzed can stay local, with no need to send it a latency-extending centralized cloud. This can save time and money while also providing, if desired, fine-grained control over data sovereignty, locality, and compliance.

Vapor IO says customers can operate at a low level with bare-metal instances, or they can use prepackaged third-party AI models and systems for specific use cases, including those for smart retail, smart manufacturing, and smart cities.
VAST Data is providing a data storage layer, a data lake, to Vapor IO’s Zero Gap AI service, with the joint offering “combining data capture, training, and inferencing at the edge.” The VAST-Vapor offering can “ perform AI at the edge in collaboration with AI performed in the centralized cloud, on-premises or in colocation datacenters,” according to VAST.

Crawford stated: “With VAST Data, we’re supercharging our Zero Gap AI platform, simplifying the deployment of AI pipelines and integrating the capabilities for these pipelines to asynchronously train, tune, inference, and retrain. This enhancement drives unprecedented value for our customers, making AI operations more dynamic and efficient than ever before.”
The two suppliers say customers can train models in a centralized datacenter or the cloud while seamlessly deploying real-time inferencing of that model at the edge, using any new data that is collected to improve the larger model continuously.
John Mao, Technical Alliances VP at VAST Data, said: “The proliferation of data requires an agile system that can span on-premises, near-premises, cloud and multi-cloud environments. The combination of these two products makes an ideal solution for enterprises looking to rapidly and cost-effectively scale their use of AI.”

As the combined VAST-Vapor technology rolls out across the US, the companies also have plans for expansion into global markets, taking advantage of VAST’s global namespace.
Neeloy Bhattacharyya, Director of Solutions Engineering for HPC/AI at VAST Data, blogged in April that VAST “provides a high-performance repository for customer data in each Zero Gap city. VAST provides multiple ways to get data on the platform ranging from traditional file and object interfaces to more modern approaches like streaming data directly by using Kafka.
“Next, it enables that data to be rapidly used to update a vector database that the AI model can in turn search very efficiently. Lastly, the VAST DataSpace ensures that all locations have access to the same data without having to constantly replicate it. This means customers who have deployed RAG-enabled AI models on Zero Gap can provide responses based on data gathered across the country without slowing down the model.”

He notes that by “VAST has integrations with tools like Apache Spark that enable users to perform table scans or generate projections from billions of rows within seconds. By leveraging the VAST DataBase to store prompt, response, user, model, vector DB and many other details, users of the Zero Gap AI platform enjoy full traceability of all AI operations.”
Vapor IO has also partnered with IBM and Comcast. IBM’s Hybrid Cloud Mesh can operate on top of the Kinetic Grid to provide interoperability between Vapor IO’s micro datacenters, with a proof of concept demo showing the Atlanta and Chicago datacenters so linked. Comcast is one of Vapor IO’s early edge network partners to link its colos with customer edge premises.
Check out Vapor IO VEM datacenter datasheets here.