Samsung has announced a second and more powerful generation of its SmartSSD Computational Storage Drive (CSD) that it says cuts scan-heavy database query processing time by more than 50 percent.
The first CSD product was introducd by Samsung in November 2020. It used a Xilinx FPGA to offload storage-related computation from its host system’s CPU. The gen 2 product uses Xilinx Versal Adaptive SoCs from AMD and, Samsung says, cuts host system energy consumption by up to 70 percent and CPU utilization by up to 97 percent.
Jin-Hyeok Choi, EVP and Head of Memory Solution Product & Development at Samsung Electronics, said: “Commercialization of the first-generation SmartSSD … established that the computational storage market has great potential. With the upgraded processing functionality of the second-generation SmartSSD, Samsung will be able to easily address increasing customer needs in the database and video transcoding sectors, as we expand the boundaries of the next-generation storage market.”

The computational storage idea is that relatively simple data processing, using highly repetitive and simple filtering, compression or format conversion operations can be carried out on a storage drive, an SSD, fitted with a local processor. This then relieves a host system of the time and energy needed to do the work itself: read data from the SSD, transfer it into the host system’s memory, have it processed by the host CPU or GPU, and then write the results back to the drive.
Samsung competitor ScaleFlux announced its third generation CSD 3000 product in November last year, and it uses an 8-core Arm processor as part of its SFX 3000 SoC. NGD and Eideticom are also developing computational storage products.
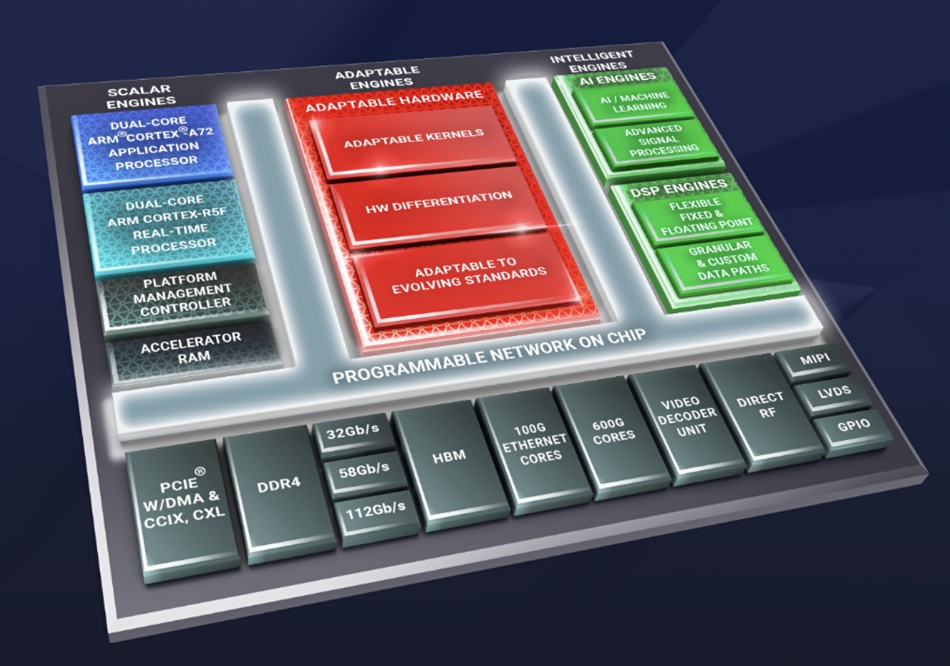
Samsung, with AMD, sold the gen 1 CSD to video communications platform providers and other IT companies. The gen 2 product uses software and intellectual property (IP) developed by these customers.
The SNA and NVM Express organisations, along with Samsung, are working to standardize computational smart SSD interface technology and the way it can be used by applications. The smart SSD operations have to be managed by and co-ordinated with the host so that the offload processing is delegated to the drive in a managed way.
Samsung expects that computational drives will find a useful role in the general AI, machine learning and 5G/6G areas. For example, drive-level intelligence could be used in image recognition and metadata tagging.








