Showa Denko (SDK) has developed a hard disk drive recording medium that will support Toshiba producing 30TB-plus drives using a Microwave Assisted Switching-Microwave Assisted Magnetic Recording (MAS-MAMR) technology suggested by Toshiba researchers.
Toshiba briefed Blocks & Files on its MAS-MAMR concept in June. MAS-MAMR can be used to narrow the recording tracks on a disk platter, so increasing the disk’s areal density and thus capacity. Toshiba uses Flux Control-MAMR in its current MG09 and MN09 18TB drives.
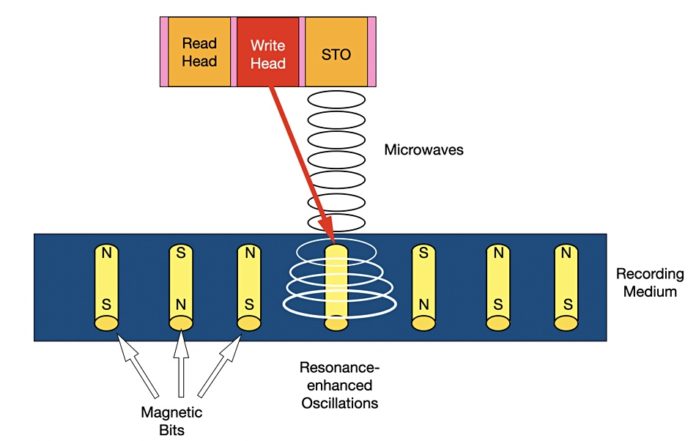
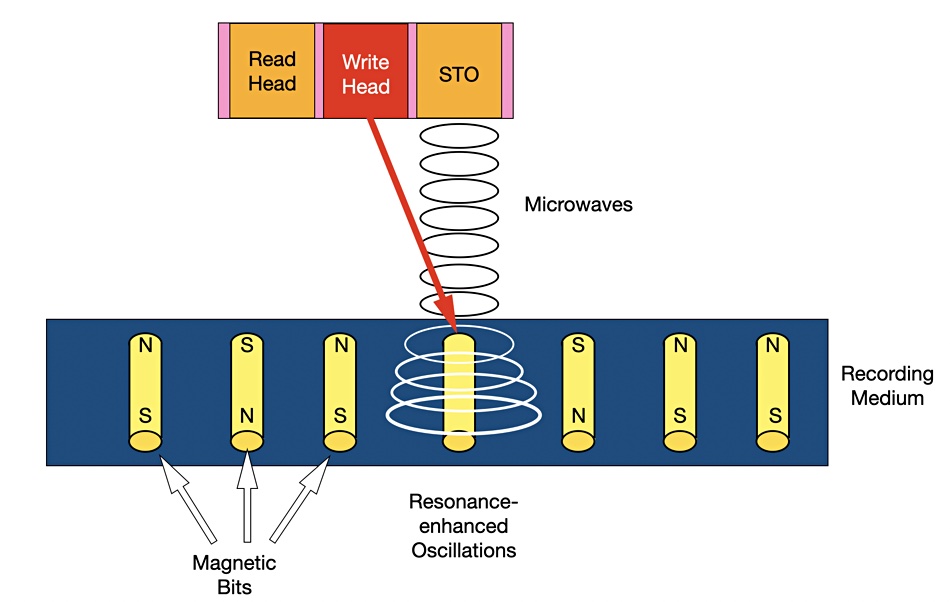
MAS-MAMR is the use of resonance-enhanced magnetic oscillations between a spin-torque oscillator (STO) in the disk drive’s read/write head and the recording medium. The stronger oscillations facilitate writing data in narrower tracks in the media.
Toshiba says that there has been a joint development program in which SDK, Toshiba, and TDK have proved that a combination of a TDK-developed read/write head equipped with dual spin-injection-layer, and disk recording media equipped with a new SDK-developed magnetic layer, “can substantially increase HDDs’ data-storage capacity through manifestations of the MAS effect.”
SDK will now accelerate development of disk media supporting MAS-MAMR so that Toshiba, using TDK heads, can develop disk drives up to and exceeding 30TB in capacity. Toshiba calls this second-generation MAMR technology.
SDK will also work on developing HAMR (heat assisted magnetic recording) media. Its MAS-MAMR announcement does not say that HAMR is a follow-on technology to MAS-MAMR but we can certainly infer that.
Comment
The road now seems open to Toshiba producing 20 to 30TB and higher capacity drives in the future, enabling it to keep up with Seagate and Western Digital as they use intermediate technologies on their own transition to HAMR drives. Both are already at the 20TB capacity level and Seagate is shipping first-generation HAMR drives, with the second generation in development. We expect Toshiba to introduce its own 20TB drive in the relatively near future.
Definitions
Resonance — the strengthening or amplification of some periodically applied force to an element when the frequency of the applied force is equal, or close to, the natural frequency of the medium containing the element, such as a bit area in a magnetic medium.
Spin Torque Oscillator — this device, referred to as an STO, produces microwaves radiating outwards. Electrons in a magnetised area have a spin state, tending to spin one way or another. By applying microwaves at the right frequency a resonance effect can alter the spin state.