NetApp and Nvidia have developed an all-flash ONTAP array/ DGX A100 GPU server AI reference architecture, pumping out up to 300GB/sec and joining DDN, Pavilion Data, VAST Data and WekaIO – which also have Nvidia-validated storage architectures.
The new ONTAP AI products come in three pre-configured sizes with 2, 4 and 8-node DGX A100 configurations. These are pre-tested and validated with AI/ML software from Domino Data Lab, Iguazio and other suppliers.
A NetApp post by Jason Blosil, a senior product marketing manager for cloud solutions, said of the move: “NetApp and Nvidia are bringing to market a new integrated solution that’s based on the field-proven NetApp ONTAP AI reference architecture. … It’s powered by NVIDIA DGX A100 systems that use second-generation AMD EPYC processors, NetApp AFF A-Series all flash storage, NVIDIA networking, and advanced software tools. You get new levels of performance and simplicity to help you more quickly deploy and operationalise AI.”
The AFF A800 array comes as a base unit and adds an expansion chassis for the 4-node config and a second for the 8-node config according to a NetApp diagram.
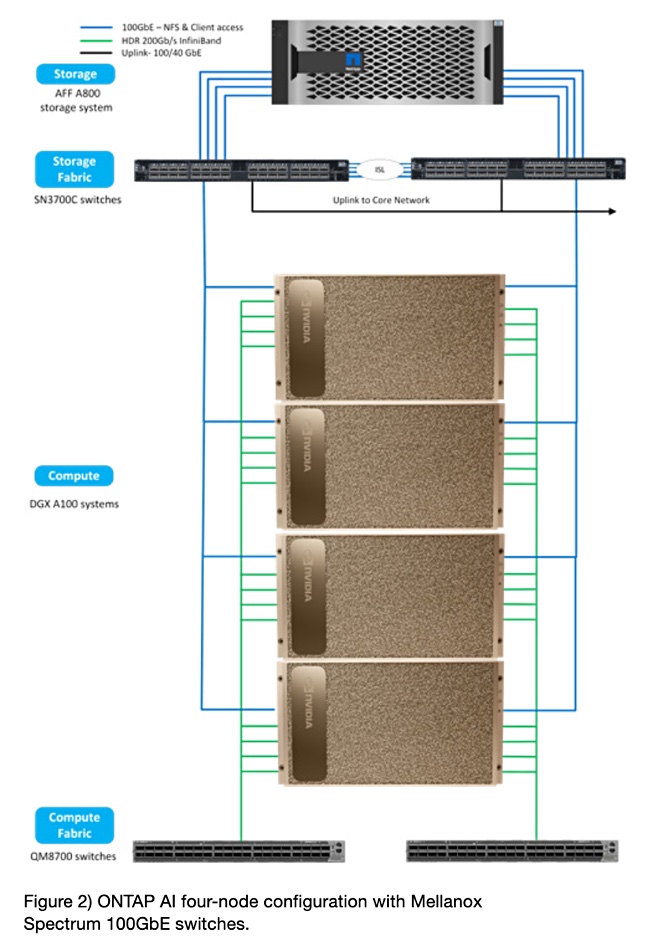
The main components are:
- NetApp AFF A-800 all-flash array in high-availability pair configuration, with 48 x 1.92TB NVMe SSDs,
- ONTAP v9,
- DGX A100 GPU server with 8 x A100 Tensor Core GPUs and 2 x AMD EPYC processors,
- Mellanox ConnectX-6 adapter interconnects – 100/200Gb Ethernet- and InfiniBand-capable,
- Mellanox Spectrum and Quantum switches, and
- separate fabrics for compute-cluster interconnect and storage access
This reference architecture does not use server CPU/DRAM GPUDirect bypass technology.
A NetApp ONTAP AI document describing the DGX-A100 reference architecture says: “With NetApp all flash storage, you can expect to get more than 2GB/sec of sustained throughput (5GB/sec peak) with well under 1 millisecond of latency, while the GPUs operate at over 95 per cent utilisation. A single NetApp AFF A800 system supports throughput of 25GB/sec for sequential reads and 1 million IOPS for small random reads, at latencies of less than 500 microseconds for NAS workloads.”
DDN, WekaIO and VAST Data also have Nvidia-validated storage architectures for DGX-A100 servers. Pavilion Data does not offer an Nvidia DGX POD reference architecture but GPUDirect and the DGX A-100. These four suppliers’ announced throughput numbers are, respectively:
- DDN – 173.9GB/sec with A1400X all-NVMe SSD system, Lustre parallel file system to a DGX-A100,
- Pavilion Data – 182GB/sec to a single DGX-A100,
- WekaIO – 163.2GB/sec to one DGX-A100 via 12x HPE DL325 servers,
- VAST Data – 173.9GB/sec to four DGX0-A100s.
An Nvidia reference architecture document says: “With the FlexGroup technology validated in this [NetApp] solution, a 24-node cluster can provide over 20PB and up to 300GB/sec throughput in a single volume.”
That is – seemingly – comfortably more than the maximum bandwidth numbers announced by DDN, WekaIO and VAST Data.
In other words, ramp up the number of A-800 arrays to lift throughput much higher. Confusingly, the actual reference architecture refers to a maximum of 8 x DGX-A100s and a single A-800 high-availability pair, not two dozen A-800 nodes. We’ve asked NetApp and Nvidia to clarify this point.
It is difficult to make exact comparisons between the NetApp, DDN, Pavilion, WekaIO and VAST Systems as the number of all-flash array systems and DGX0-A100 servers differ between the various suppliers’ reference architecture configurations and explanatory documents.
Potential buyers would be well advised to extract such configuration details from the suppliers so as to make an informed choice.
More information is available in a blog from NVIDIA and a very nicely detailed Nvidia reference architecture document (registration required.)