Google Cloud is adding immutable and indelible backups, central backup management, and the ability for developers to apply backup policies when a Compute Engine VM is created.
Google Cloud has a Backup and Disaster Recovery service that protects Compute Engine virtual machines (VMs), VMware VMs, databases and file systems, providing app-consistent backups. Protected databases include IBM Db2, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, SAP ASE, SAP HANA, SAP IQ, SAP MaxDB, and PostgreSQL. The new backup vault prevents deleting or modifying backups, helping to secure backup data against malicious and accidental data loss. The centralized backup management tool should make backup admin easier and improve Compute Engine VM creation by developers with simultaneous backup policy setting.
How it works
A Google blog, which Blocks & Files saw before these features were announced, notes: “Backup vault data is stored in a Google-managed project and is logically air-gapped from your self-managed Google Cloud project.”
“The underlying backup vault resources are not visible or accessible to users in your organization, which prevents direct attacks against those resources. Access to backup vault data is provided exclusively through Google Cloud Backup and DR service APIs and UI.”
The backup vault is created in the Google Cloud console and can have a retention time frame set for immutability and indelibility. Vaulted backups are fully self-contained and enable recovery even when the source resource is no longer available. Backup vaults can be created in a different project from the source project in which a protected Compute Engine VM is running. That means the backup can still be accessed if the source project has been deleted.
The blog explains: “This supports immediate recovery of production applications to pre-existing or newly created projects, including recovery into projects configured as isolated recovery environments (IREs) for pre-recovery testing/forensics in the aftermath of a cyber attack.”
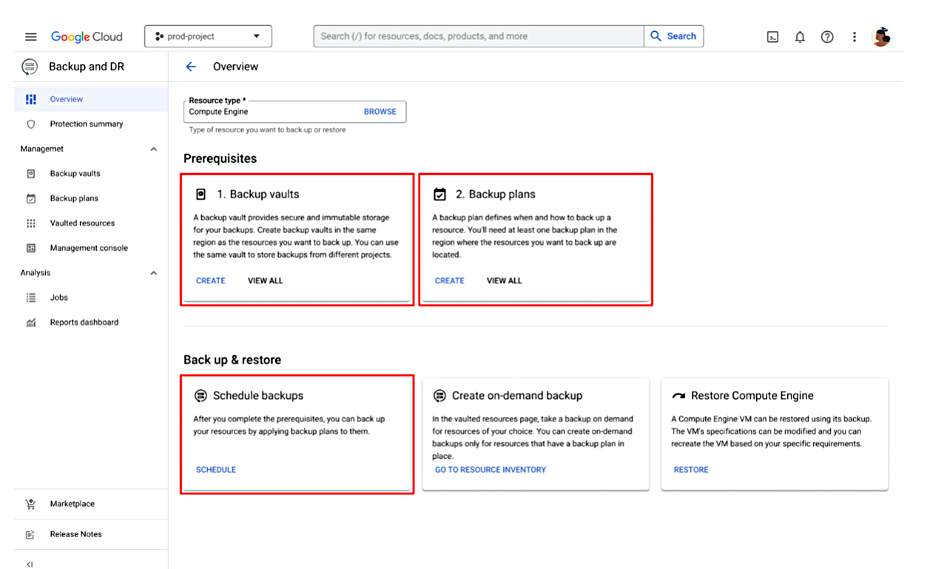
The centralized backup management facility initially supports Compute Engine VM protection. This involves first setting up a backup vault, then defining a backup schedule, and then applying it. The blog declares that this “approach eliminates the need for complex configurations.”

This central dashboard-like facility can monitor job success, failure, and progress, tracking the status of scheduled backup jobs to ensure they run as expected. It can generate detailed reports on failed and skipped jobs, protected resources, compliance, storage usage, and more. The facility can also be used to set up alerts and notifications to stay informed about backup events.
Google claims: “The backup service enhances both governance and oversight by offering centralized control over backup policies while allowing application owners to manage their own backup tasks.”
It says the new backup offering facilitates easy integration into a customer’s automation workflows – whether they’re using gcloud CLI, APIs, or Terraform.
Availability
The backup vault feature is available today in preview, and will be generally available in the coming months. It supports protection for Compute Engine VMs, VMware Engine VMs, Oracle databases, and SQL Server databases. Learn more about backup vaults and secure protection for VMs and databases here.