Chinese NAND manufacturer Yangtze Technology Memory Corporation (YMTC) has extended the endurance of QLC flash to match that of TLC.
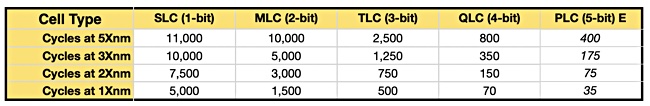
YMTC is beset by US technology export restrictions on the fabrication equipment it can import. Nevertheless, it has developed Xtacking gen 4 232-layer 3D NAND – comparable to the latest from competing suppliers such as Micron (232-layer), Samsung (236-layer), SK hynix (238-layer), and Kioxia/Western Digital (218-layer). YMTC’s 232-layer die features QLC (4bits/cell) flash that has a raw endurance of about 1,000 program/erase (P/E) cycles compared to the 4,000–5,000 or so of TLC (3bits/cell).
QLC NAND cells, with a third more capacity than TLC cells, are more efficient on a $/TB basis but counter that with slower performance and a shorter working life. The cell-level raw endurance cannot be altered. However, by careful management of how data is written to the population of cells in a QLC SSD, evening out their wear, and judicious over-provisioning of cells to provide replacements for worn-out ones, the overall QLC SSD endurance can be increased.
The YMTC tech was reported by the Chinese language IThome media outlet. It claims YMTC’s X3-6070 features 128-layers, Xtacking gen 3 technology, and supports 4,000 P/E cycles.
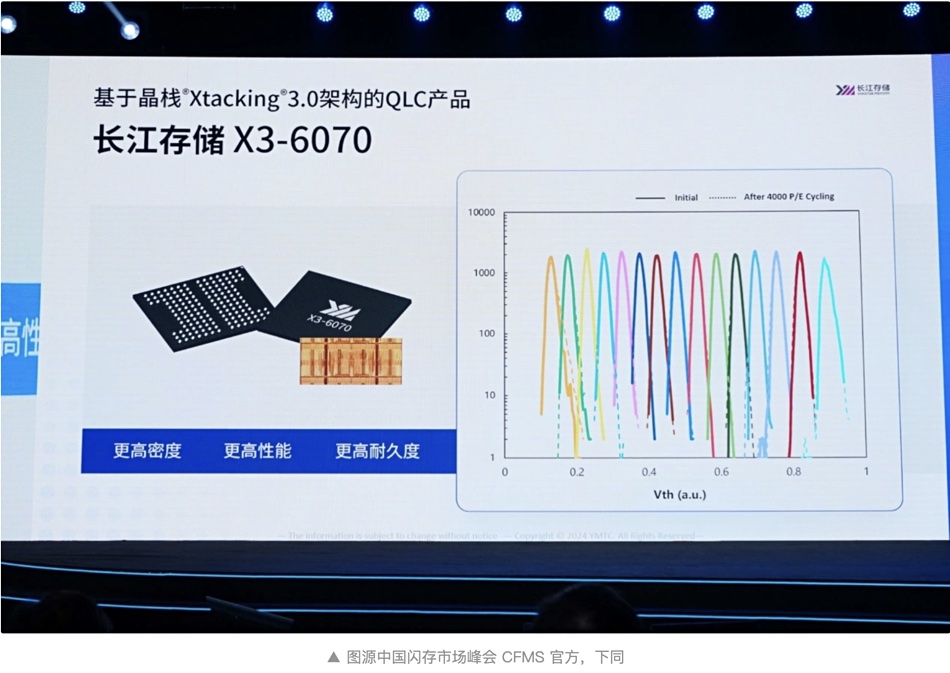
The IThome report indicates that the gen 3 Xtacking tech allows for more flexible voltage modulation. There are no details on how YMTC has extended its QLC NAND’s endurance, though.
YMTC explains that X3-6070 has an I/O speed increase of 50 percent, and 70 percent more storage density than its prior generation of QLC technology. When used in PBlaze7 7340 SSDs, it makes them usable for enterprise-level storage and mobile phone workloads. A consumer-grade PC41Q (PCIe 4 x 4, NVMe 1.4) drive built with this QLC flash has a sequential read and write bandwidth of 5,500 MB/sec. It also features one year of data retention and has a 2 million hours MTBF rating at 30°C.
YMTC is not alone. Solidigm has a DC-P5430 QLC SSD, which has a 14 percent longer endurance than TLC SSDs from Kioxia, Micron, and Samsung for sequential workloads. This enables lower overall write I/Os to the drive, compared to a more random workload where the endurance drops to almost half that of the TLC drives – 0.58 drive writes per day instead of one. The YMTC report makes no mention of workload restrictions on the endurance-raising technology.








