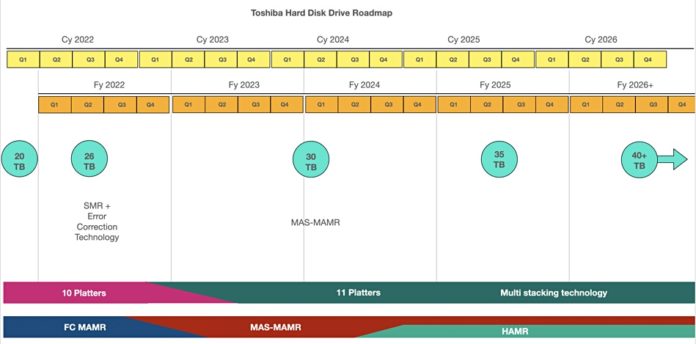
Toshiba revealed its roadmap out to 40+ TB hard disk drives in an Investor Relations Day presentation showing it has 11-platter HAMR drives in its plans.
The February 8 presentation outlined the product strategy by a proposed Device Co. spin-off and was given by Hiroyuki Sato, Toshiba’s overall CEO and President, and Seiichi Mori, his CTO. They provided unprecedented detail on Toshiba’s HDD operation – not least its actual growing market share in the nearline HDD market; high-capacity, 7,200rpm, 3.5-inch disk drives:
- FY 2016 – 8 per cent
- FY 2019 – 11 per cent
- FY 2021 Q4 – 17 per cent
It aims to increase this to 25 per cent in its FY2025 and then to reach 30 per cent in what it calls the near term. The company says it is continually developing its Philippines HDD plant and is starting HDD production at a second plant in China. The planned market share gains will come from adding more capacity to its disk drives by using a combination of multi-stacking platter technology and energy-assisted magnetic recording.
Toshiba has just announced its MAS-MAMR (Microwave Assisted Switching Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording) technology, and intends to introduce Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording (HAMR) in its FY2024.
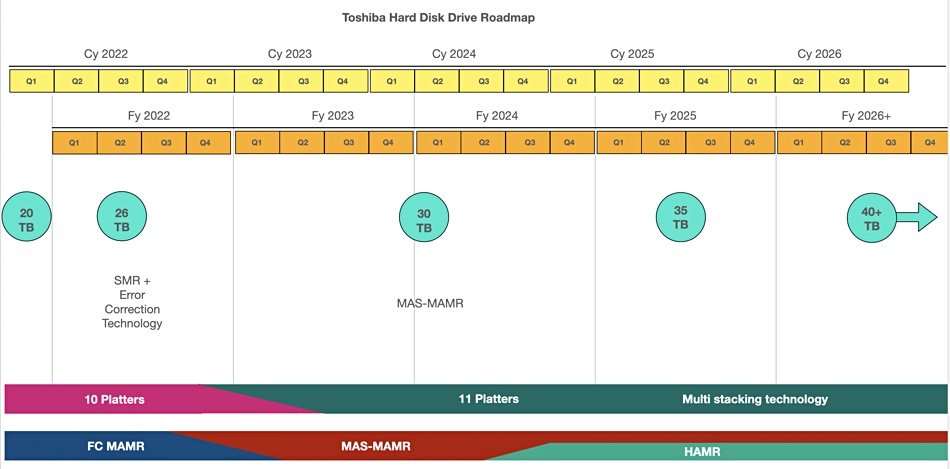
We combined the detail from two of the presentation slides to create the roadmap chart below:
Seagate and Western Digital are currently shipping 20TB disk drives. Bearing that in mind, Toshiba’s maximum capacity HDD is currently 18TB. The first new drive, to be announced quite soon, is a 20TB product using the same FC-MAMR (Flux-Controlled Microwave-Assisted Magnetic Recording) technology as in its 18TB drives which have 9x 2TB platters.
Extending the platter count to ten will produce a 20TB drive. Toshiba’s presentation deck said that development of a 10-platter drive is already complete and mass production will start in fy2022.
The next development will be a FC-MAMR 26TB drive in FY2022, again using 10-platter technology, but SMR (Shingled Magnetic Recording) – 2.6TB per platter. This involves overlapping wider write tracks to increase the narrower read track density. The downside of this is that rewriting data involves reading a zone of tracks including the data to be rewritten, editing in the new data, and then rewriting the entire zone. All this takes longer than simply writing new data to empty tracks, and the process has to be managed by the drive or by the host server, which means software changes.
Around the cross-over from FY2023 to FY2024, Toshiba plans to introduce a 30TB drive using MAS-MAMR technology and 11 platters, meaning 2.73TB/platter. The presentation slide does not say this is an SMR drive. The 30TB drive will be qualified in FY2023 and shift to mass production in FY2024. The 11-platter technology is currently under development.
In FY2025 we should see a 35TB drive with 11 platters (3.9TB/platter) and using either MAS-MAR or HAMR technology or both – the slide is unclear and implies both will be used. Toshiba says basic HAMR R&D is ongoing and a prototype drive will be available in FY2024.
This will be followed by 40+ TB products out past FY2026.
Seagate and Western Digital
How does this roadmap compare to what we know of Seagate and Western Digital?
Seagate has said it hopes to ship a 50TB HAMR drive in its FY2025 and a 100TB drive by (FY) 2030. A 30TB drive will come along before the 50TB one – say in the 2034/2024 period. The company’s fiscal year ends on July 3 of the same number calendar year. Thus Seagate’s FY2022 will end on July 3, 2022 and started on July 4 2021 – quite different from Toshiba’s fiscal years.
The 50TB Seagate drive will arrive – if it arrives – roughly when Toshiba has its 35TB drive planned, putting Toshiba at an immense capacity disadvantage. The 30TB Seagate drive could arrive in the same general period as Toshiba’s 30TB drive.
Western Digital’s roadmap includes a 30TB HAMR drive and an 11-platter archival disk drive. We have derived a roadmap from CEO David Goekeler’s comments at a virtual Wells Fargo TMT Summit 2021 that took place on November 30, and it looks like this:
- 2022 — 24TB
- 2023 — 26TB
- 2024 — 28TB
- 2025 — 30TB
These are calendar years and it’s our estimate, not published WD data. Toshiba will be at 26TB (SMR) in CY2022 and 30TB in CY2024, giving it an apparent lead on WD.
This leaves us asking a big question: can Seagate deliver a 50TB drive in its FY2025 (July 4, 2024 to July 3, 2025)? If it can then it looks to have an enormous looming capacity advantage over both WD and Toshiba.
Toshiba must know of this Seagate roadmap and, notwithstanding that, it hopes to grow its nearline HDD market share to 25 per cent in the CY2025 period and then increase it further in the years after that. Does it doubt Seagate’s ability to deliver a 50TB drive before July 2025?
No pressure then, Seagate.
Footnote: Toshiba’s presentation deck said nothing about multi-actuator drives, which have been mentioned by both Seagate and Western Digital as a way of increasing disk I/O speed.