E3.L – an EDSFF storage bay form factor. See EDSSF entry.
EDSFF
EDSFF – Enterprise and Data centre SSD Form Factor colloquially known as rulers. There is an SNIA EDSFF work group, the SFF Technology Affiliate Technical Work Group (SFF TA TWG), made up from 15 storage industry suppliers. The initial version of the specification was created by the SNIA SFF Technology Affiliate organization as a response to concerns about solid state data center storage and ways of optimising capacity, thermal properties and physicalmsize for different applications.
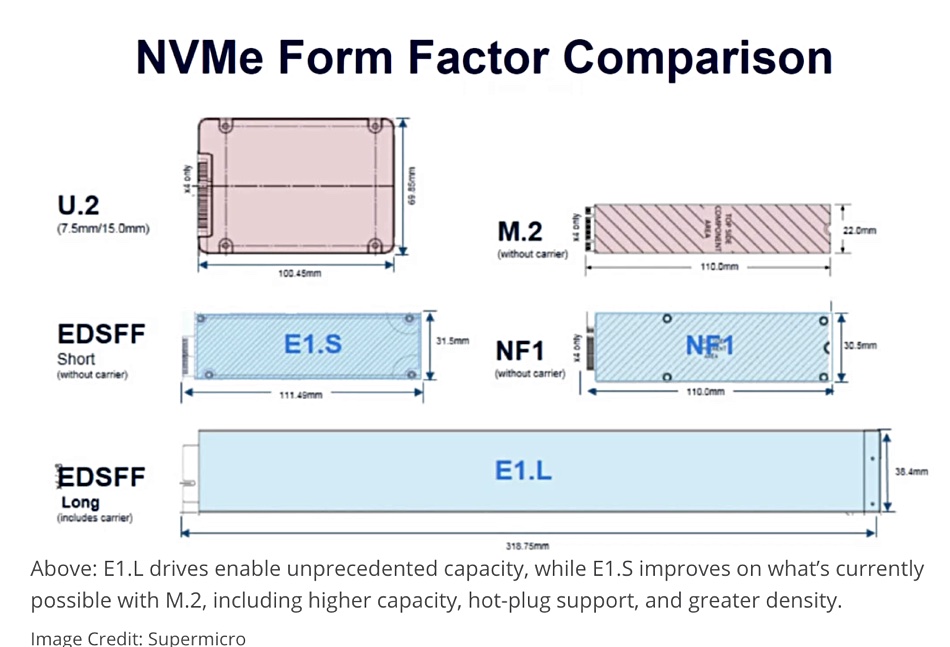
The idea is to move away from 2.5-inch and 3.5-inch disk-bay sizes for SSDs, which now come in these sizes as well as M.2 gumstick cards and PCIe add-in card (AIC) formats. There will be instead longer and thinner devices, the so-called rulers, which can provide up to 1PB of capacity in a 1U server, using 64-layer, TLC 3D NAND. Here is a table showing the EDSFF formats;

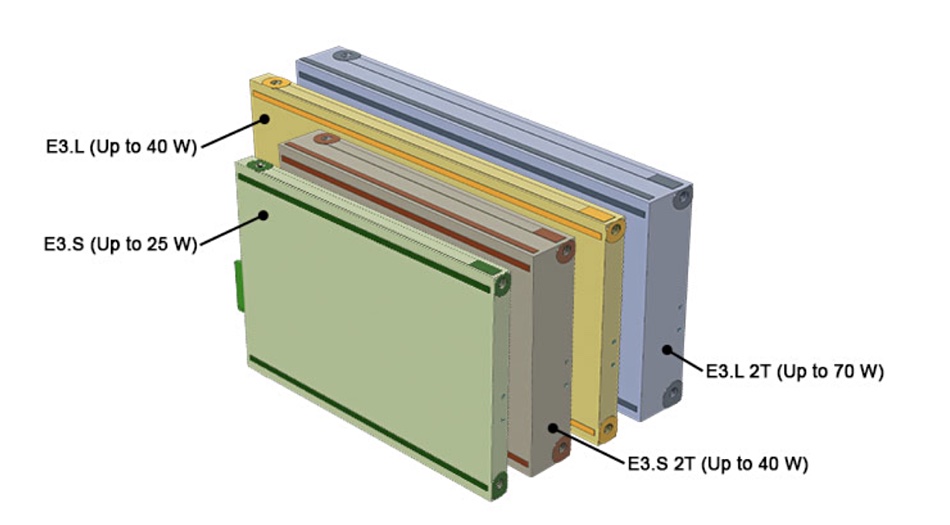
There are two basic formats, E1 and E3. Both come in short and long variations, with the E3.S and E3.L formats also having T variations. E3 SSDs support up to 16 PCIe lanes with power profiles of up to 70W. The E3.S form factor updates and replaces the U.2 2.5-inch drive format, inherited from 2.5-inch disk drive days.
The EDSFF is also working on a 3-inch form factor that is 76mm (3 inches) wide. This format has two thicknesses and two lengths: 7.5mm or 16.8mm thick and either 104.9mm or 142.2mm long. Download the format specs here.
A Supermicro diagram illustrates some of these form factors;
LRDIMM
LRDIMM – Load Reduced DIMM memory module. Such DIMMs can have up to eight ranks or blocks of memory. They have a memory buffer instead of a register like RDIMMs (Register DIMMs). The memory buffer is used to consolidate the electrical loads of LRDIMM ranks to a single electrical load on the motherboard, enabling the up to eight ranks on a single DIMM module, and helping configure systems with the largest possible memory capacity. LRDIMMs use more power and have higher latencies compared to the lower capacity RDIMMs. LRDIMM memory chips are used in servers in data centers, cloud computing, and high-performance computers.
JSON
JSON – Java Script Object Notation is a self-describing file and data interchange format using text to transmit and store data objects. JSON data is formed from name/value pairs written in between double quotes like this: “lastName”:”Doe”. Because its syntax is similar to JavaScript object code, a JavaScript program can convert JSON data into native JavaScript objects and process them.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster Recovery – the switching on of a second remote data center when a first data center stops functioning due to a disaster, such as a drastic fire, flood, explosion, earthquake or other major event. In order for this switchover to take place a secondary data center has to be in existence and ready to be switched on.
This secondary data center should be geographically remote from the first data center so that it is not destroyed by the same event, such as a hurricane or earthquake. It needs to have the same set of servers, storage devices , network switches, etc., and system and application software so that client systems connected to the damaged data center can be redirected to the disaster recovery (DR) site and continue operating. That requires the stored databases, files and objects to be synchronized between the main and secondary data centers.
It also requires that there be a DR plan which is kept updated and regularly tested to ensure that it works. DR sites are thus expensive to set up and operate, and so often only initiated for mission-critical applications and their IT resources. If the main data center runs its mission-critical applications using virtual machines then these VMs could be re-instantiated in a public cloud, with its facilities used as required for the DR site, a virtual DR site and not a physical one. The same would be true where a data center runs entirely on cloud-native, containerized applications, with containers re-instantiated in the cloud.
An alternative arrangement is to have two data centers, physically remote from each other but otherwise identical, act as reciprocal DR sites for each other, with some amount of IT resource capacity held in reserve at each site for that eventuality.
DWPD
DWPD – Drive Writes per Day – refers to the endurance of an SSD, as in writing data in the amount of its total capacity size before it wears out in a warranted period, typically 5 years, although it could be shorter. A 1DWPD rating for a 15TB SSD mean that it can sustain having 15TB of data written to it daily for its warranted period. An alternative way of presenting an SSD’s endurance (working life) is to say that it supports a fixed number of TB written (TBW). A 15TB SSD with a 26,700TBW rating will last for 5 years at a 15TB/day writing rate.
dStorage
dStorage – Decentralized or Web3 storage. This takes the virtual equivalent of an object storage system and stores data fragments on globally distributed nodes owned by independent operators who are paid using cryptocurrency, with storage I/O transactions recorded using blockchain.
DRAM
DRAM – Dynamic Random Access Memory – composed from cells in a solid state array which can have a positive or negative charge, signalling binary one or zero values. The charge, stored in a capacitor, has to be constantly refreshed by electricity , and it is lost when the power is switched off; hence it is dynamic or volatile. The cells can be individually addressed – randomly addressed – as opposed to stored locations on a tape which have to be serially addressed as the tape streams through a drive.
DRAM consists of billions of cells laid out in a square array. Each cell needs a transistor, a source with a bit line connection, a gate with a word line connection, a capacitor to store charge, and a drain. The capacitor is above the drain.
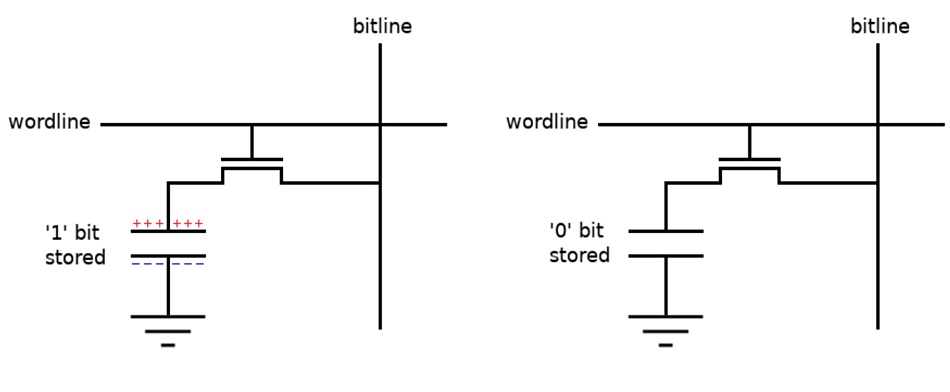
The transistor is used to charge or discharge the capacitor. The word line is used to switch the cell on or off and the bit line is for reading and writing data.
DRaaS
DRaaS – Disaster Recovery as a service. An IT-using organization may have a remote disaster recovery (DR) data center set up to take over when its main data center is hit by a disaster and stops operating. This involve the cost of setting up, equipping and operating the remote center. An alternative is to have it hosted in a public cloud and supplied as a service. This means that the organisation does not need to own the remote data center site and equipment nor recruit and manage the staff there, relying on the service provider instead and, hopefully, saving cost.
Codec
Codec – Compression/Decompression chip that compresses or decompresses a stream of audio or video data.

