HBA – Host Bus Adapter. See entry for that.
Host Bus Adapter
Host Bus Adapter – A block interface device to connect a server’s PCI bus to a Fibre Channel, SCSI or SATA network linking it to a block storage device. HBAs, in other words, are used to connect servers to SANs. They exist at the server and SAN end of the network link and, in the Fibre Channel situation, support a specific generation of Fibre Channel. They are generally backwards-compatible with prior generations.

HBAs can link direct to a destination HBA or to intervening switches or directors (major switches) which aggregate FC links.
HB
HB – Hellabyte. One thousand yottabytes. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
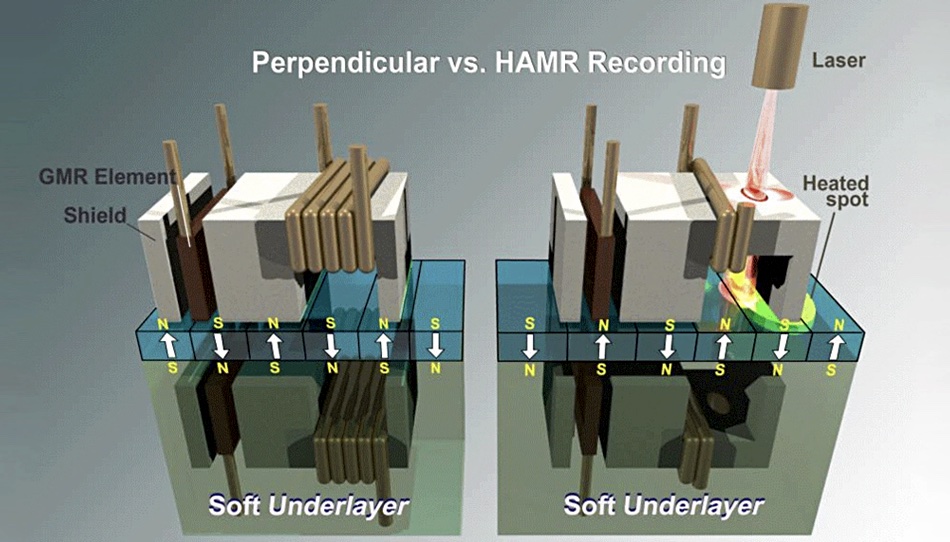
HAMR
HAMR – Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording technology which uses laser-produced heat to create smaller bits on disk drive platters than conventional magnetic recording (PMR), that are stable at room temperature, unlike similar-sized PMR bits.
Gigabyte
Gigabyte – 1,000 megabytes. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
Gibibyte
Gibibyte – 1,024 mebibytes. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
GiB
GiB – Gibibyte – 1,024 mebibytes. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
GB
GB – Gigabyte – 1,000 megabytes. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
Gb
Gb – Gigabit – 1,000 megabits. See Decimal and Binary Prefix entry.
GPUDirect RDMA
GPUDirect RDMA – Graphics Processing Unit Direct Remote Direct Memory Access – Nvidia protocol introduced in 2017 to enable network interface cards to bypass CPU host memory and directly access GPU memory. A forerunner of GPUDirect.
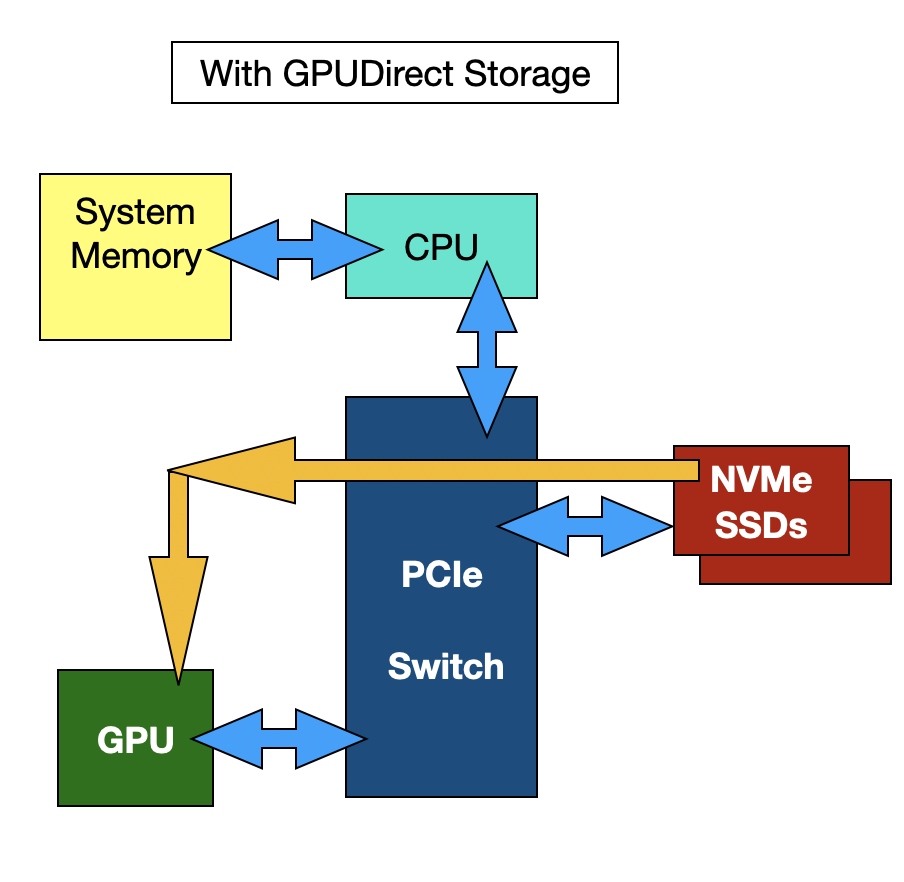
GPUDirect
GPUDirect – GPUDirect enables DMA (direct memory access) between GPU memory and NVMe storage drives. Typically, data transfers to a GPU are controlled by the storage host server’s x86 CPU. Data flows from storage that is attached to a host server into the server’s DRAM and then out via the PCIe bus to the GPU. Nvidia says this process becomes IO bound as data transfers increase in number and size. GPU utilisation falls as it waits for data it can crunch.
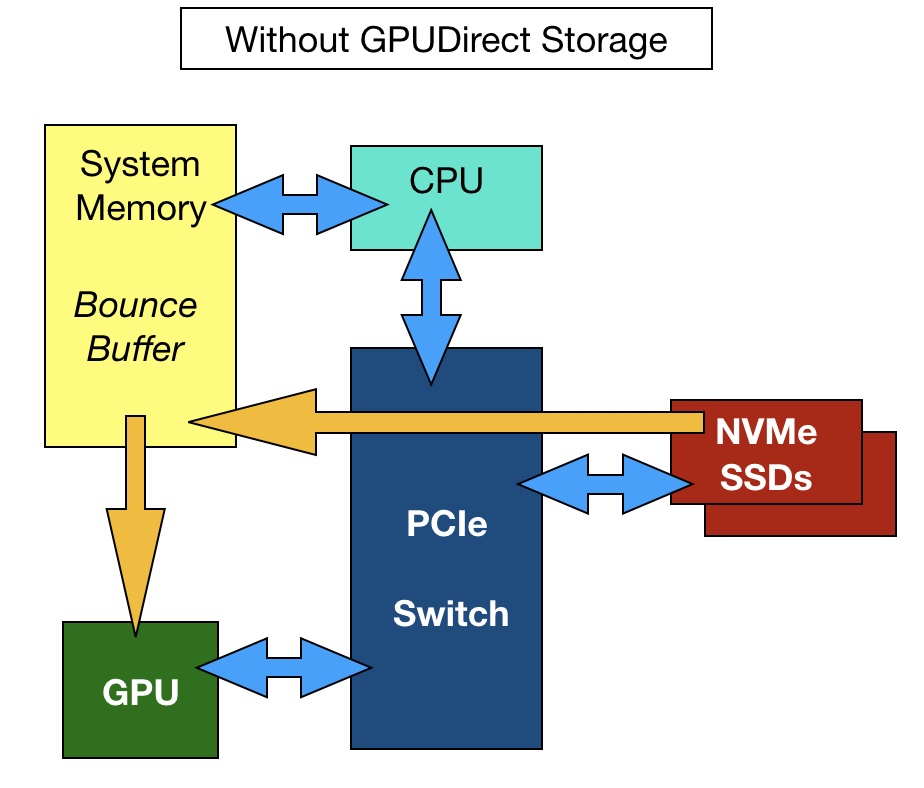
With GPUDirect architecture, the host server CPU and DRAM are no longer involved, and the IO path between storage and the GPU is shorter and faster. The storage drives may be direct-attached or external and accessed by NVMe-over-Fabrics.