Robot – a mechanism in a tape library for moving tape cartridges to and from tape drives.

Robot – a mechanism in a tape library for moving tape cartridges to and from tape drives.

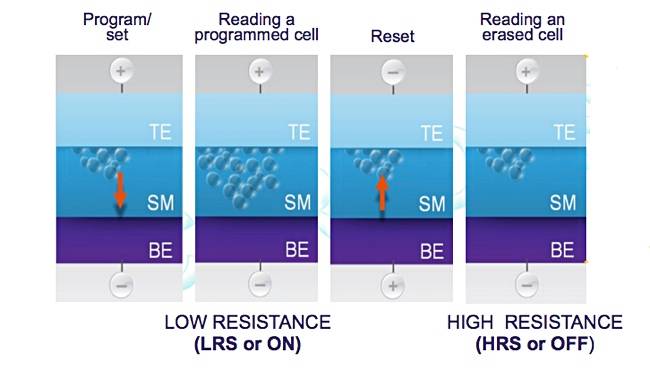
ReRAM – Resistive RAM – this a fast non-volatile storage-class memory relying on the formation of electrically conducting oxygen vacancy filaments through an otherwise insulating medium. Research discovered that sending a current through silicon oxide could counteract its inherent insulator property and create a silicon crystal (oxygen vacancy) pathway or filament. Electrical pulses could then break and re-connect this filament, changing the resistance levels from low to high – the binary signalling mechanism. ReRAM is said to be as fast to read as SRAM (static random access memory), but lower cost with reduced power consumption and non-volatility. Weebit Nano, Intrinsic Semiconductor Technology and CrossBar are developing ReRAM products. All three use a silicon oxide base material and a crosspoint-style architecture.
Replication – The copying at a block level of data in a source volume or file system to a target system. When first set up there is an initial synchronisation between the source and target systems and then every block-level change on the source system will be copied to the target system. It is possible to have file-level replication but that is inefficient as a single block-level change will trigger an entire file replication.
A synchronous replication system replicates any changes to the target system before telling the source system that the data has been written. Asynchronous replication creates a queue of changes and carries them out in order but not necessarily straight away when a change is registered in the target system. This does not affect the performance of the target system but the replicated copy will be out of step with the source until the queue of changes is empty and no more changes in the source system have taken place.
RDIMM – Registered Dual Inline Memory Module. Unlike a standard (unbuffered) DIMM the RDIMM features a a hardware register that buffers the DIMM control signals but not the application data, between the memory controller and the memory chips to help stabilize and manage the electrical load of the memory modules. This increases the DIMM’s reliability by putting less of an electrical load on a memory controller. It enables RDIMMs to support larger memory capacities than is possible with UDIMMs. RDIMMs are mostly found in workstations and servers as they provide better reliability and stability.
RDMA over IP– Remote direct memory access using IP across a network. When data is requested or sent an RDMA protocol is used between the two networked devices, but the data is split into chunks and sent as an IP packet with IP headers — so that standard IP networks can handle the traffic flow control and provide lost packet recovery.
RDMA – Remote Direct Memory Access. A technique to load data directly into the memory of a remote device without transiting the source or destination device’s storage IO system. RDMA is much quicker than storage IO thorough an operating system’s storage IO stack..
RAS – Reliability, Availability, Serviceability. Reliability means the ability of a computer hardware or software item to perform according to its specifications. Availability is the ratio of time a system or component is functional to the total time it is required or expected to function. Serviceability refers to the ease with which a component, device or system can be maintained and repaired. The RAS acronym and term was originally devised by IBM in connection with its mainframe systems.
RAS – Reliability, Availability, Serviceability. Reliability means the ability of a computer hardware or software item to perform according to its specifications. Availability is the ratio of time a system or component is functional to the total time it is required or expected to function. Serviceability refers to the ease with which a component, device or system can be maintained and repaired. The RAS acronym and term was originally devised by IBM in connection with its mainframe systems.
Ransomware – Malicious code used by hackers to penetrate an organisation’s IT network, find its storage and then encrypt stored data. The victim organisation is them told to pay a ransom, typically in cryptocurrency, to obtain a decryption key. An alternative ransomware attack method is to exfiltrate data with a ransom payment needed to get it back or keep it private.
RAIL – Redundant Arrays of Independent Libraries – a tape library architecture. RAIL provides parallel access to multiple tape libraries that can be geo-distributed, and have high availability and scalability. A 3-geo system has three separate libraries in geographically dispersed locations. It is a RAID-like scheme providing increased scale, protection and performance for tape libraries.
RAID – Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. Disk drives can fail, in which case their data contents are lost. RAID is a way of countering this by combining disk drives into logical units to provide resilience against drive failure with data recoverability and even faster drive performance. Parity schemes can also be used to help recover otherwise lost data on a failed drive. There are various ways of doing this; the so-called numbered RAID levels, with each level providing its own mix of resilience and performance. The cost of RAID levels is that some portion of the overall combined group of disk drive’s capacity, known as the overhead, is used to provide the RAID level features. Here is a table showing some RAID levels;
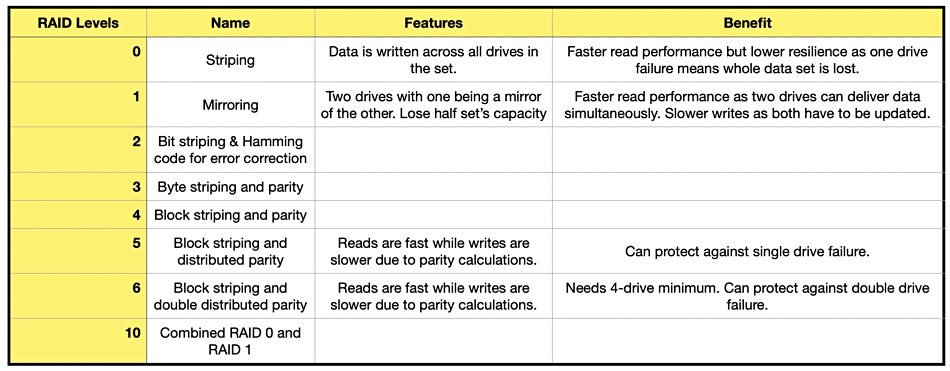
RAID 5 can protect against a single drive failure in configurations with 3 or more drive. RAID 6 can protect against a double drive failure in configurations of 4 or more drives.
A hardware RAID card can carry out parity calculations, offloading the host CPU and speeding otherwise slower disk IOs. When a disk in a RAID set fails it needs to be rebuilt – using a spare drive, and this rebuild can take hours, if not days, with modern high capacity drives, such as 18, 20 and 22TB drives. A 16TB disk drive rebuild can take 24 hours. The higher the capacity the longer the rebuild time.