MemVerge reckons customers could cut their cloud app carbon emissions by using its Memory Machine Cloud software with per-workload emissions tracking.
Its Memory Machine Cloud software enables users to submit jobs to the AWS cloud in a serverless way and have them run in EC2 Spot instances, with dynamically modified sizes as needed to economize on cloud resources. The Memory Machine Cloud Essentials edition is free and includes a WaveWatcher calculator to track cloud app carbon emissions of cloud apps so organizations can right size for a lower carbon footprint.
MemVerge COO Jon Jiang said: “For companies focused on reaching carbon neutrality, real-time measurement of carbon emissions for each workload is an essential capability. The telemetry works hand-in-hand with real-time right sizing that has the potential to drive the emissions of datacenter servers down 10 percent industry wide.”
Memory Machine Cloud’s latest release, v2.3, has the ability to put an app to sleep, then restart where you left off. MemVerge says that data scientists were faced with the choice of leaving their cloud instance running all night or shutting down and restarting their apps built with popular integrated development environments (IDE) like RStudio and Jupyter. Sleep and WaveRide from within an IDE.
The Memory Machine software now includes IDE Sleep and Wakeup widgets for popular IDEs such as RStudio that allow data scientists to put their apps to sleep or use WaveRider continuous right sizing from within RStudio.
A Memory Machine Cloud WaveWatcher service builds on its ability to track CPU, memory, network, storage IO usage by application, to calculate carbon emissions. The data can then be used by the WaveRider service to automatically right size resources and reduce CO2 footprint.
MemVerge has defined a three-step blueprint to lower cloud app carbon emissions. Step one is to migrate apps from your datacenters to the public cloud, AWS in this case. That’s because, according to GoClimate.com, the Kg CO2 / year / server for cloud servers is approximately half that of on-prem servers.
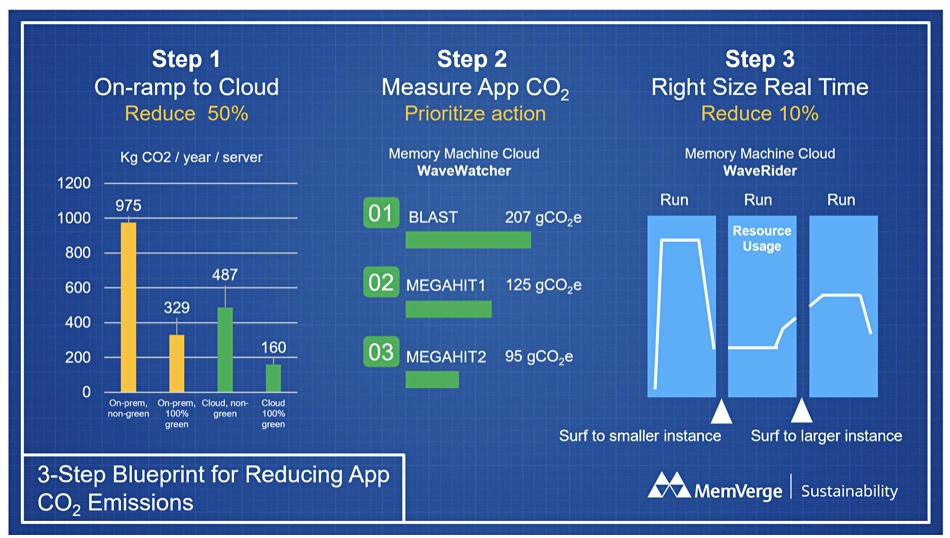
Step two is to track cloud app carbon emissions by using tools like the Memory Machine Cloud WaveWatcher service. This profiles app resource usage and identifies opportunities for right-sizing optimization, such as enabling automatic runtime workload moves to smaller or larger instances based on their real-time resource needs.
Step three is to do this right-sizing continuously. It will cost though, as you have to upgrade from the free Memory Machine Cloud Essentials to Memory Machine Cloud Pro to get WaveRider continuous right sizing. This is charged on a 25 percent of savings pay-as-you-go basis.
Comment
This looks interesting but is limited to AWS. We think that his limitation may be removed by MemVerge in the future. Also there are no examples of saved carbon emissions by named applications, which is a pity. The chart above does show some generic type savings but there are no details. No doubt the MemVergers will produce them soon enough.








