GPUDirect RDMA – Graphics Processing Unit Direct Remote Direct Memory Access – Nvidia protocol introduced in 2017 to enable network interface cards to bypass CPU host memory and directly access GPU memory. A forerunner of GPUDirect.
GPUDirect
GPUDirect – GPUDirect enables DMA (direct memory access) between GPU memory and NVMe storage drives. Typically, data transfers to a GPU are controlled by the storage host server’s x86 CPU. Data flows from storage that is attached to a host server into the server’s DRAM and then out via the PCIe bus to the GPU. Nvidia says this process becomes IO bound as data transfers increase in number and size. GPU utilisation falls as it waits for data it can crunch.
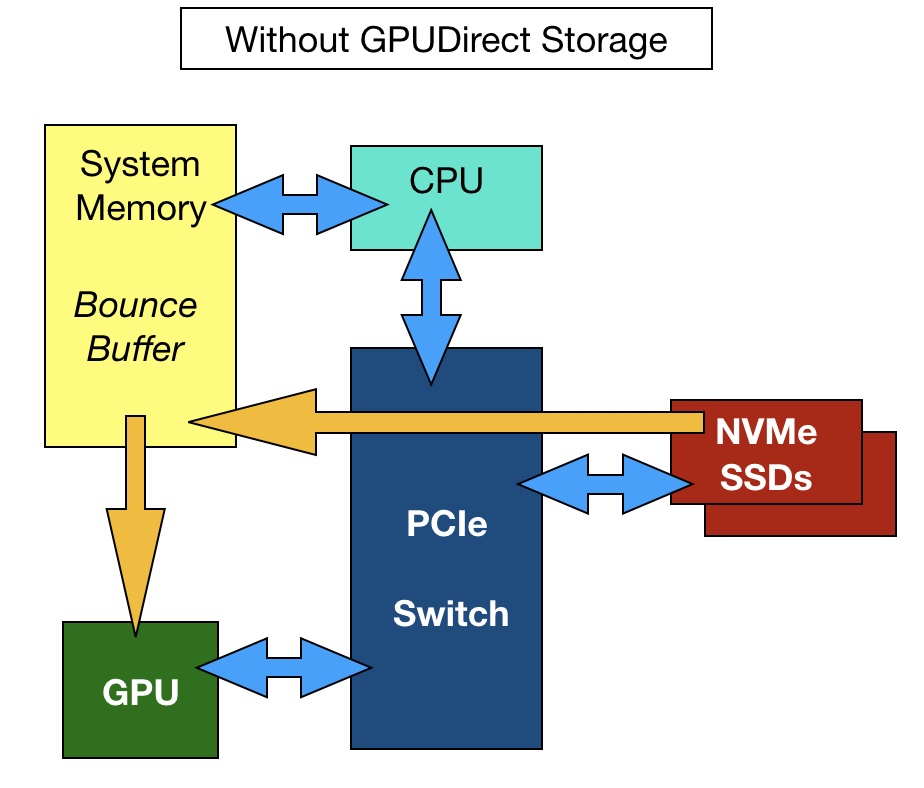
With GPUDirect architecture, the host server CPU and DRAM are no longer involved, and the IO path between storage and the GPU is shorter and faster. The storage drives may be direct-attached or external and accessed by NVMe-over-Fabrics.
GPU
GPU – Graphics Processing Unit – a hardware processor with many parallel elements for computing the aspects of a player’s surroundings in a video game or the appearace of a building or scene in a picture or video. Such processors have found a role in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications where billions of repetitive calaculations need to be carried out. They are better at this than standard x86 general purpose processors.

GDDR

GDDR – Graphics Double Data Rate memory – DRAM from graphics computing units (GPUs). Micron makes GDDR6 memory which pumps out data at 616GB/s of bandwidth to a GPU. Its GDDR7 product, sampling in June 2024, delivers 32 Gb/s of high-performance memory, and has over 1.5 TB/s of system bandwidth, which is up to 60% higher bandwidth than GDDR6, and four independent channels to optimize workloads. Its GDDR7 also provides a greater than 50% power-efficiency improvement compared to GDDR6 to better thermals and lengthen battery life, while the new sleep mode reduces standby power by up to 70%.
FTP
FTP – File Transfer Protocol. It is a way to transfer file between a source computer system and a destination computer system across a a TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) network link.
FTL
FTL – Flash Translation Layer – code resident in an SSD’s controller which manages data placement -writing – and reading on an SSD and the recovery and re-use of cells containing deleted data. This is known as garbage collection.
FRU
FRU – Field-Replaceable Unit – a maintenance term meaning that a part of a system can be replaced where the system is deployed (in the field) without the system having to be transported to a service center.
FPGA
FPGA – Field-Programmable Gate Array. These are semiconductor devices built from a matrix of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) linked by programmable interconnects. This means that FPGAs, unlike ASICs, can be reprogrammed to carry out new application or functionality requirements after manufacturing. Some smartNICS are developed by using FPGAs first, then ASICs and ultimately general purpose CPUs.

Floating Gate
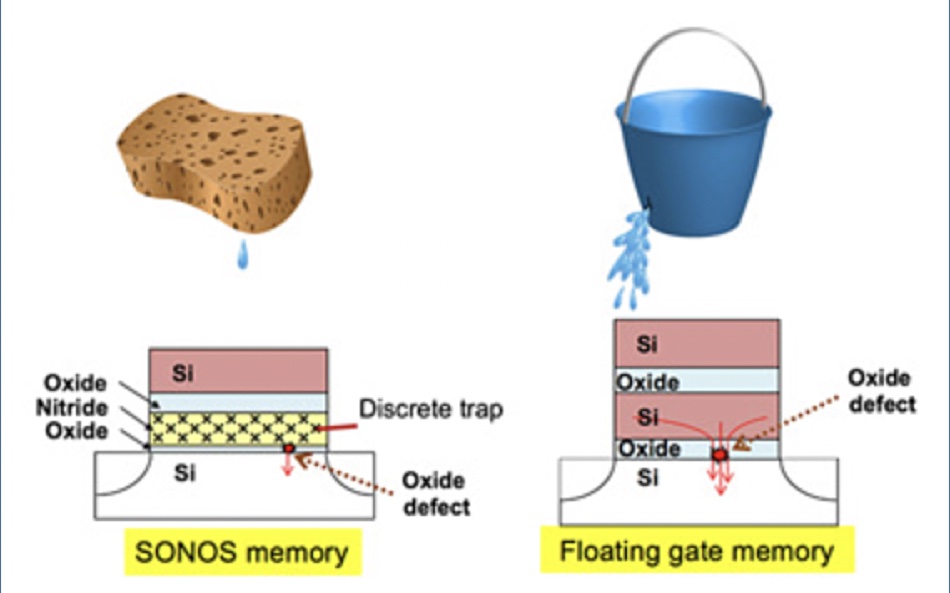
Floating Gate – A type of integrated circuit NAND cell invented in 1967 by Simon Sze of Bell Labs, which uses floating gate transistors. These have a polycrystalline silicon conductive layer, isolated between insulating (dielectric) layers, which can store electrons. The electrons are trapped in the floating gate but can be driven out by a high enough electrical current. The gate’s binary value floats between 1 and 0 depending on whether electrons are in the isolated layer (1) or have been driven out (0).
Flash
Flash – A generic term for NAND-based storage. See NAND.
Filer
Filer – A storage array using SSDs or disk drives or both to store files in folders and make them available to many accessing servers and/or personal computing devices using a network protocol such as NFS.
File
File – a file is set of data items, such as this document, with a name and an entry in a nested file and folder structure. This starts from a so-called root directory which contains entries for sub-directories or folders or files. A folder can, in turn, contain sub-folders or files and so on with a file-folder structure capable of having 100s of levels and billions of files. A file-folder structure is implemented on desktop and notebook computers and can also be implemented on servers. A shared storage device holding files is called a filer or NAS, Network-Attached Storage system, and it is accessed using the Unix Network File System (NFS) or Windows Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. CIFS (Common Internet File System) is an SMB dialect.