Toshiba this week confirmed it will deliver both conventional and shingled MAMR hard drives.
Scott Wright, director of HDD marketing at Toshiba America Electronic Components, told us MAMR will be used to “advance the capacity of both CMR (discrete track) recording and to SMR (shingled track) recording.”
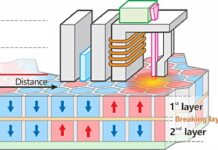
He added: “In theory, MAMR does not advance long-term areal density gain as far as what may be achievable with HAMR. MAMR is certainly the next step; HAMR is very likely an eventual future step up the AD (areal density) ladder.”
Areal Density
WD is adding shingled recording to its MAMR disk drives to increase areal density – and so capacity – to 16TB and then 20TB and beyond. MAMR SMR Drives are not drop-in replacements for conventionally recorded PMR disk drives but WD will also ship lower-capacity non-shingled MAMR drives. WD is also still researching HAMR and could move across to that technology eventually.
Seagate’s own energy-assist technology, HAMR (Heat-Assisted Magnetic Recording) will not, so far, use shingling.
Toshiba is investing in MAMR and HAMR and other magnetic recording technologies, and is working collaboratively with the leading storage heads and media vendors. It is less vertically integrated than Seagate and Western Digital which make their own components.
Toshiba said it would adopt MAMR at an investor conference in November 2018.
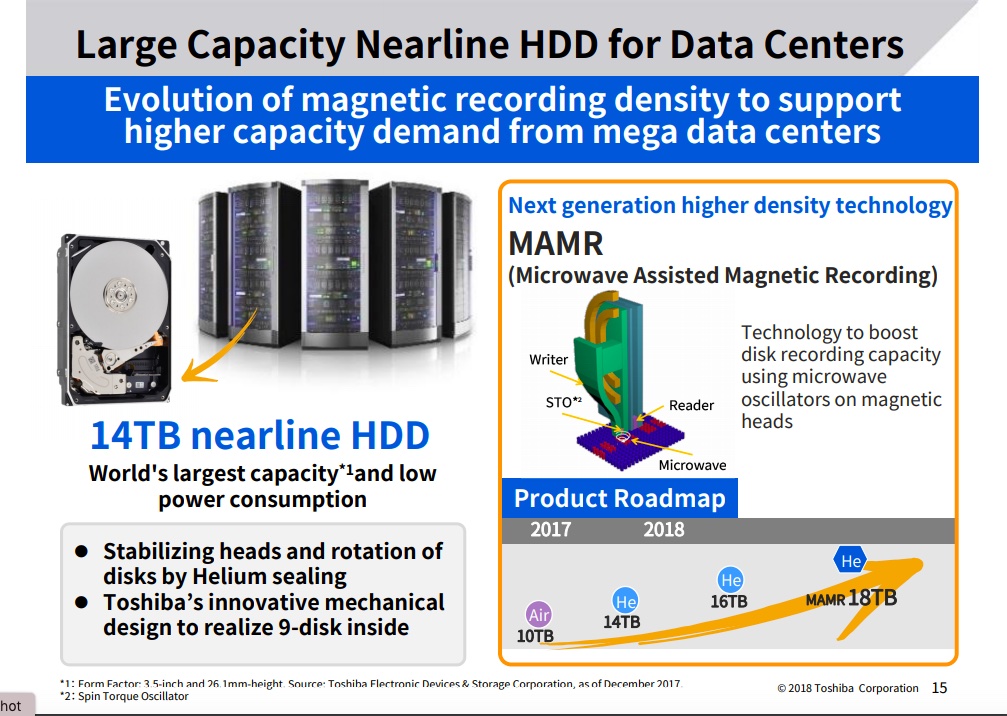
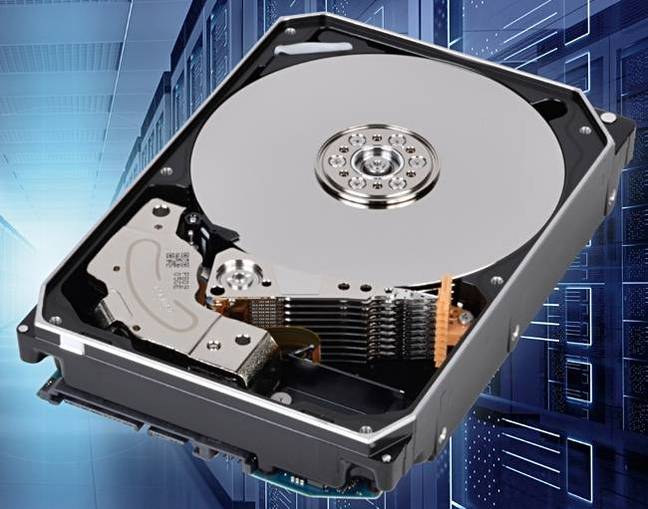
Its high-capacity 3.5-inch helium-filled drives have nine platters inside, compared with eight for WD and Seagate. This gives Toshiba more disk platter surface area to play with.
Wright told Blocks & Files: “In January we announced our 9-disk 16TB MG08 family (using TDMR.) Since our MG08 announcement, both TDK (heads technology) and Showa Denko (media technology) have made their own announcements about their components being used in the Toshiba’s MG08 16TB generation.”

TDMR is Two-Dimensional Magnetic Recording, using two disk read heads to get a better read signal.